O98.7
DESCRIPTION
HIV is currently the commonest cause of maternal deaths in South Africa. Transmission of HIV from mother to infant may occur during pregnancy, delivery and/or breastfeeding. Without intervention, 25–40% of infants born to HIV-infected women may become infected. With appropriate interventions, maternal mortality as well as perinatal transmission of HIV can be substantially reduced. In South Africa, 4% of women who were initially HIV-negative become positive later during pregnancy. Repeat HIV testing is essential.
For comprehensive information on the care of HIV-infected pregnant women refer to the current National Consolidated Guidelines for the Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV (PMTCT) and the management of HIV in Children, Adolescents and Adults as well as the current Guidelines for Maternity Care in South Africa.
GENERAL MEASURES
HCT in all pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Provide routine counselling and voluntary HIV testing to all pregnant women at their very first antenatal visit, and treat other STIs if necessary.
- All women who test negative must be offered repeat HIV testing every 3 months throughout pregnancy, at labour/delivery, at the 6-week EPI visit and 3 monthly throughout breastfeeding.
Women who choose not to be tested
- Provide with individual ‘post-refusal’ counselling and offer HIV testing at every subsequent visit.
- Perform a TB symptom screen at each visit.
- Counsel on risks of MTCT to unborn baby, HIV risk reduction behaviour and offer HIV prevention services.
Pregnant women who test HIV positive
- Confirm result with a 2nd rapid HIV test of another type in compliance with current HCT policy.
- If results are discordant, repeat both first and confirmatory rapid HIV tests and if still discordant, send blood for a laboratory HIV ELISA.
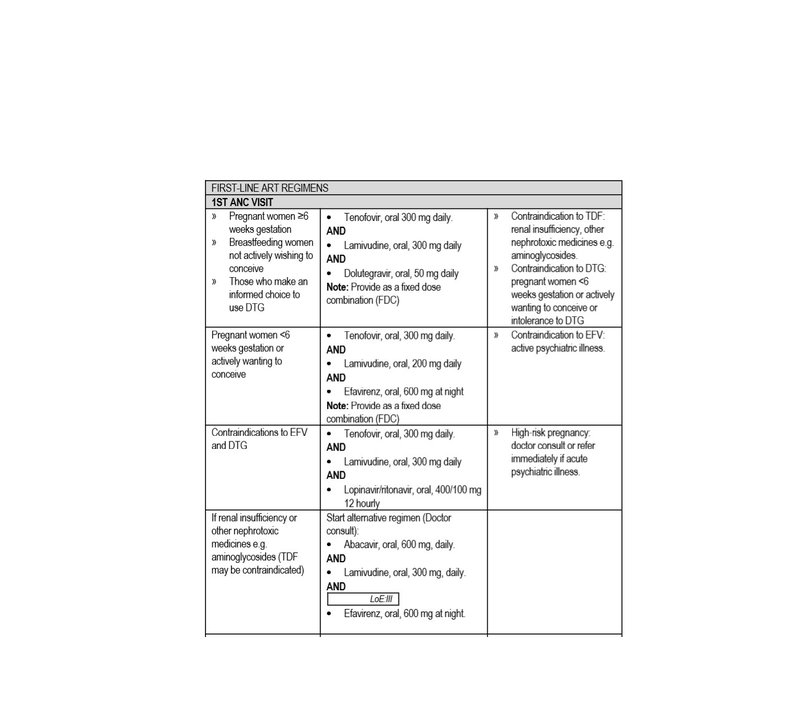
- All confirmed HIV-infected women must be fast-tracked for ART regardless of CD4 count.
- Perform clinical staging and TB symptom screen, and take a blood sample for CD4 cell count and creatinine, on the day of testing. Obtain results within a week.
- If CD4<100 cells/mm³ , do a serum cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) test.
- Start ART on the day of diagnosis (unless there are symptoms of TB).
- Investigate all those with TB symptoms before ART initiation. If TB treatment is started, defer ART for 2 weeks.
- HIV-infected women must return 1 week after their initial ANC visit to get their creatinine and CD4 cell count results and be managed accordingly
- Refer women with unwanted pregnancies < 20 'weeks’ gestation for termination of pregnancy (TOP) services.
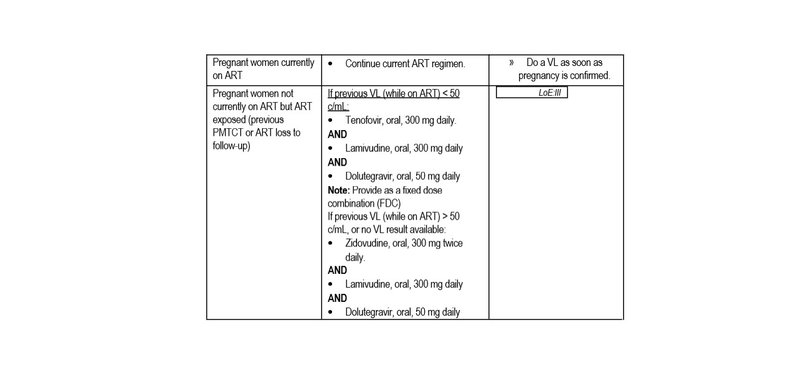
Pregnant women already known to be HIV-infected
- If not on ART, do clinical staging; take blood for CD4 count (to determine eligibility for cotrimoxazole prophylaxis) and creatinine. If CD4< 100 cells/mm³, do a serum cryptococcal antigen (CrAg) test. - Start ART the same day if no contraindication.
- If already on ART for > 3 months, take blood for viral load irrespective of when it was last done.
Antenatal support
- Counsel about the importance of adherence and virological suppression for PMTCT.
- Counsel on infant feeding, safer sex, family planning, postnatal contraception, partner testing, routine cervical cancer screening.
- Perform TB symptom screening at each visit.
- Provide appropriate nutritional care and support including iron, folate and calcium supplementation and Hb testing.
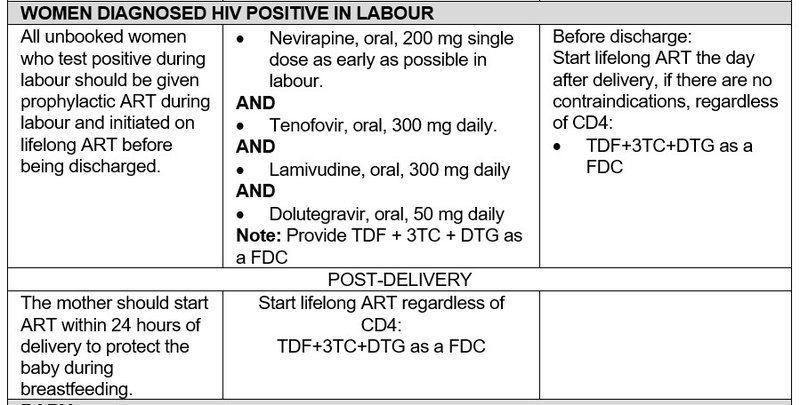
Postpartum support
- Provide adequate support and counselling, particularly addressing ART adherence during breastfeeding.
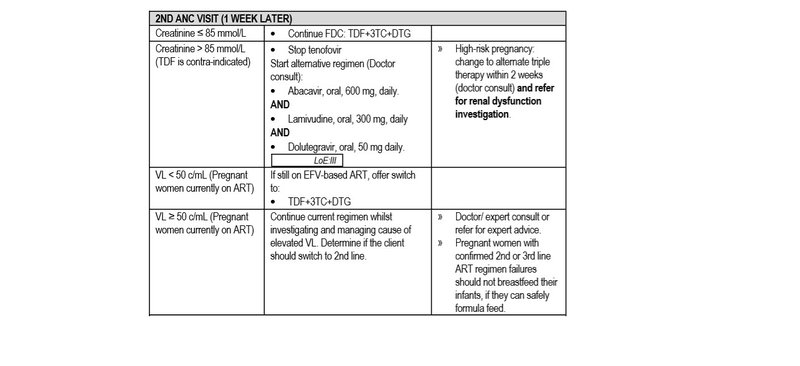
- Educate mothers about the benefits of breastfeeding. Only in circumstance where the mother has confirmed 2nd or 3rd line ART regimen failure, advise not to breastfeed and prescribe replacement feeds.
- Refer mother to appropriate services to continue lifelong ART as part of the general adult ART population.
MEDICINE TREATMENT
Opportunistic infection treatment and prophylaxis for HIV-infected pregnant women:
Pregnant women diagnosed with pulmonary TB:
- First line TB treatment is safe and effective in pregnant women.
- See Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) in adults) .
Pregnant women on ART with no symptoms of TB:
Women with CD4 ≤ 200 cells/mm³ or WHO clinical stage 2, 3 or 4:
- Cotrimoxazole, oral, 160/800 mg daily, until CD4 > 200 cells/mm³ .
If CrAg-positive consult an infectious disease expert, or refer
See Cryptococcosis
Although fluconazole should be avoided in the 1st trimester, pregnant women should be counselled that the benefits of fluconazole outweigh the risks in the management of cryptococcosis.
All pregnant women <20 weeks gestation exposed to fluconazole should have an ultrasound scan to detect congenital abnormalities.
Fluconazole is present at concentrations similar to maternal plasma concentrations in breast milk.
Also see Antiretroviral therapy
BABY: See The HIV-exposed infant to decide whether infant is low risk or high risk and what HIV prophylactic management is needed.
Note:
- eGFR and creatinine clearance are not reliable for diagnosing renal impairment in pregnancy.
- Monitor response to ART within 3 months of ART initiation with a plasma VL. If VL is not suppressed, refer or consult for expert advice.
Viral load monitoring for 1st line regimen in pregnant and breastfeeding women:
Newly diagnosed and initiated ART for the first time:
- Do 1st VL at 3 months on ART.
- If VL < 50 c/mL, repeat VL at delivery.
Known HIV-positive women already on ART:
- VL at first/booking visit in ANC,
- If VL < 50 c/mL, repeat VL at delivery.
Known HIV-positive women, who are not currently on ART, but are ART exposed (e.g. previous PMTCT, or ART loss to follow-up) and who are initiating a DTG-containing regimen:
- Do 1st VL at 3 months on ART.
- If VL < 50 c/mL, repeat VL at delivery.
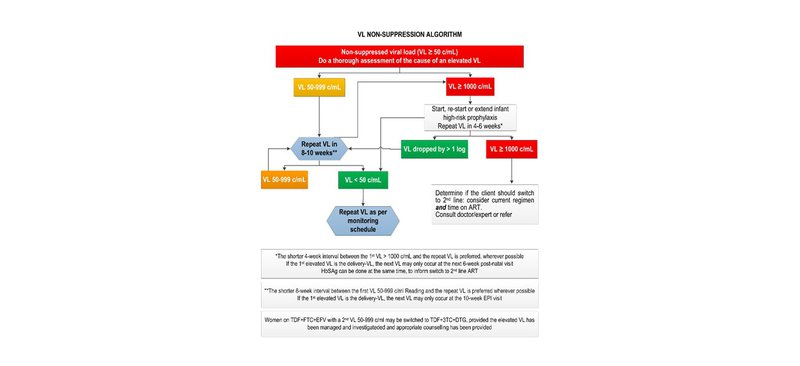
If the VL is ≥ 50 c/mL in any of the above scenarios, manage as per the VL non-suppression algorithm below.
REFERRAL
- Refer mothers suspected of non-adherence early.
Urgent
- Creatinine > 85 mmol/L.
- ALT > 100 IU/L.
- Pregnant women who are CrAg+, and
- LP cannot be performed,
- symptomatic (headache, confusion), or
- asymptomatic, but in the 1st trimester.