O98.1
DESCRIPTION
A sexually transmitted infection with many manifestations that has a latent phase and may be asymptomatic in pregnant women. It is caused by the spirochaete, T pallidum . Vertical transmission to the fetus occurs in up to 80% of cases in untreated mothers. Untreated maternal syphilis may lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, non-immune hydrops fetalis, or congenital syphilis in the newborn.
DIAGNOSIS
- All pregnant women should have a syphilis test at the first booking visit.
- Women who booked in the first trimester and tested negative should have a repeat test done around 32 'weeks’ gestation.
- Diagnosis is made by positive serology. There are 2 types of diagnostic tests.
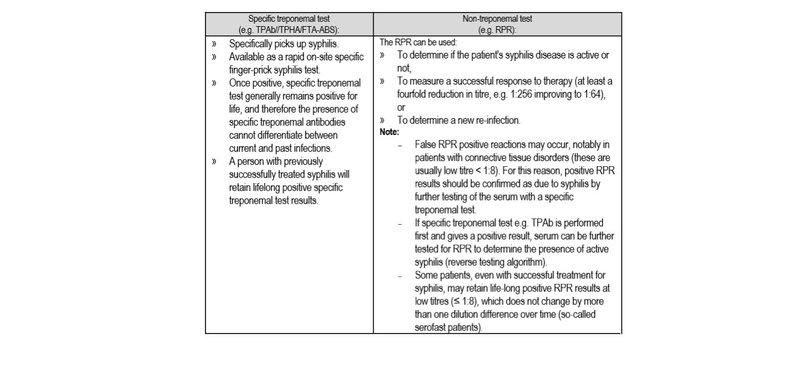
GENERAL MEASURES
- Encourage partner notification and treatment.
- Provide counselling and promote HIV testing.
- Educate on treatment adherence.
- Promote condom use.
MEDICINE TREATMENT
Pregnant woman
- Benzathine benzylpenicillin, IM, 2.4 MU weekly for 3 weeks.
- Reconstitute with 6 mL of lidocaine1%without adrenaline (epinephrine).
- Follow up at 3 months after the last injection to confirm a fourfold (i.e. 2 dilution) reduction in RPR titres, provided the initial titre was ≥ 1:8. If initial titre < 1:8, further reductions may not occur (serofast reaction).
Severe penicillin allergy: (Z88.0)
Refer for in-patient penicillin desensitisation.
Newborn baby
If baby asymptomatic, well and mother not fully treated > 1 month before delivery, give:
- Benzathine benzylpenicillin (depot formulation), IM, 50 000 units/kg as a single dose into the lateral thigh.
CAUTION
Benzathine benzylpenicillin (depot formulation) must never be given intravenously.
REFERRAL (baby)
- Mother was not treated
- Mother has received < 3 doses of benzathine benzylpenicillin
- Mother delivered within 4 weeks of commencing treatment
- Baby has any of the following
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Pseudoparesis
- Snuffles
- Oedema
- Jaundice
- Anaemia
- Purpura
- Desquamative rash (especially involving palms and soles)