A09.0/A09.9
DESCRIPTION
A sudden onset of increased frequency of stools that are looser than normal, with or without vomiting. Commonly caused by a virus, but may be caused by bacteria or parasites. The cause of acute diarrhoea cannot be diagnosed without laboratory investigation. It may be an epidemic if many patients are infected at the same time.
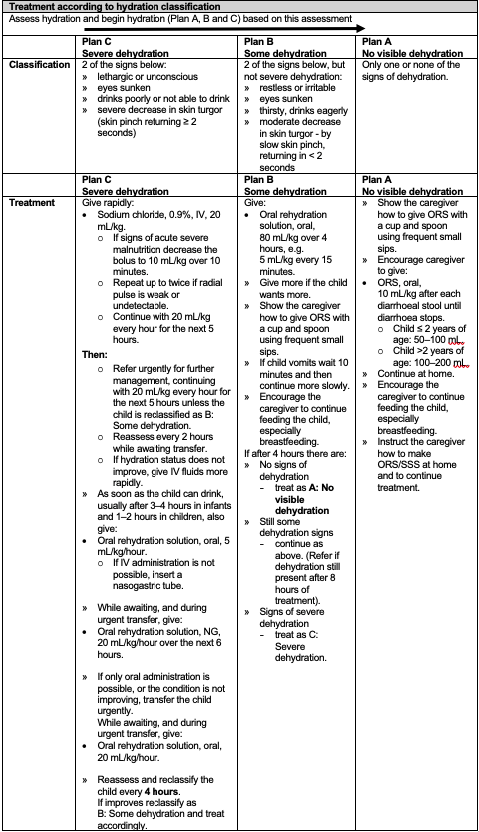
Assess and manage dehydration according to the table below.
Children with severe dehydration require referral. Begin management for dehydration immediately whilst awaiting referral (see below).
All children should be assessed and treated for associated conditions e.g. hypothermia, convulsions, altered level of consciousness, respiratory distress, surgical abdomen.
Special types of diarrhoea
- Bloody diarrhoea: consider dysentery. See: Dysentery.
- Diarrhoea with high fever or very ill: consider typhoid. See: Typhoid fever.
- Persistent diarrhoea. See: Diarrhoea, persistent in children.
- Diarrhoea in children in the context of an adult epidemic: consider cholera. See: Cholera.
Child should return immediately if:
- condition does not improve
- fever develops
- condition deteriorates
- eyes sunken
- poor drinking or feeding
- slow skin pinch
- blood in stool
MEDICINE TREATMENT
The following children should receive ceftriaxone prior to referral:
- Neonates with severe dehydration.
- Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) AND severe dehydration or shock.
- Ceftriaxone, IM, 80 mg/kg/dose immediately as a single dose. See: paediatric dosing tool.
- Do not inject more than 1 g at one injection site.
CAUTION: USE OF CEFTRIAXONE IN NEONATES AND CHILDREN
- If SUSPECTING SERIOUS BACTERIAL INFECTION in neonate, give ceftriaxone, even if jaundiced.
- Avoid giving calcium-containing IV fluids (e.g. Ringer Lactate) together with ceftriaxone:
- If ≤ 28 days old, avoid calcium-containing IV fluids for 48 hours after ceftriaxone administered.
- If > 28 days old, ceftriaxone and calcium-containing IV fluids may be given sequentially provided the giving set is flushed thoroughly with sodium chloride 0.9% before and after.
- Preferably administer IV fluids without calcium contents.
- Always include the dose and route of administration of ceftriaxone in the referral letter.
In all children who are able to take oral medication
- Zinc (elemental), oral for 14 days:
- If < 10 kg give 10 mg/day.
- If > 10 kg give 20 mg/day.
Homemade sugar and salt solution is recommended for home use and to prevent dehydration.
Homemade sugar and salt solution (SSS)
½ level medicine measure of table salt
plus
8 level medicine measures of sugar
dissolved in 1 litre of boiled (if possible) then cooled water
(1 level medicine measure = approximately 1 level 5 mL teaspoon)
REFERRAL
- Severe dehydration. Failure to maintain hydration on oral fluids/feeds (failed Plan B).
- Children with general danger signs, e.g.:
- convulsions
- altered level of consciousness
- intractable vomiting
- inability to feed or drink
- Children with dysentery if:
- < 12 months of age
- signs of dehydration
- Malnourished children.
- Suspected acute abdomen or other surgical problem.